How to restore Collagen in the body
The body combines amino acids to create collagen or any other protein. According to the Cleveland Clinic, you can obtain amino acids by consuming and digesting protein-rich foods such as meat, beans, and dairy products. The body will then convert the amino acids into collagen.
Your body uses vitamins and minerals, specifically vitamin C, zinc, and copper, during the collagen repurposing process. These nutrients are typical components of a healthy diet. They can be found in abundance in the foods you consume. Vitamin C is found in citrus fruits, red and green peppers, tomatoes, broccoli, and greens. Meats, shellfish, nuts, whole grains, and beans are excellent mineral sources.
However, as you age, your body may no longer absorb or synthesize nutrients as efficiently. To ensure that your body has sufficient ingredients to produce collagen, you may need to alter your diet or take nutritional supplements.
What is Collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant type of protein in the human body and an essential component of the skin. Numerous tissues contain it, including muscles, bones, tendons, blood vessels, and the digestive tract. It is essential for many bodily processes, including wound healing.
What effect does collagen have on the skin?
When levels of collagen are high, the skin is soft, smooth, and resilient. Collagen aids in the renewal and repair of skin cells. Collagen levels and quality have an effect on the skin. As a person ages, their body produces fewer types of collagen, and the quality of collagen in the body declines.
This can result in:
a loss of elasticity in the skin and other connective tissues lines, wrinkles, and skin laxity joint rigidity.
As people age, changes in the structure of collagen weaken the bond between the skin’s various layers. This may explain why people develop wrinkles and other signs of aging skin (1).
Collagen Depletion
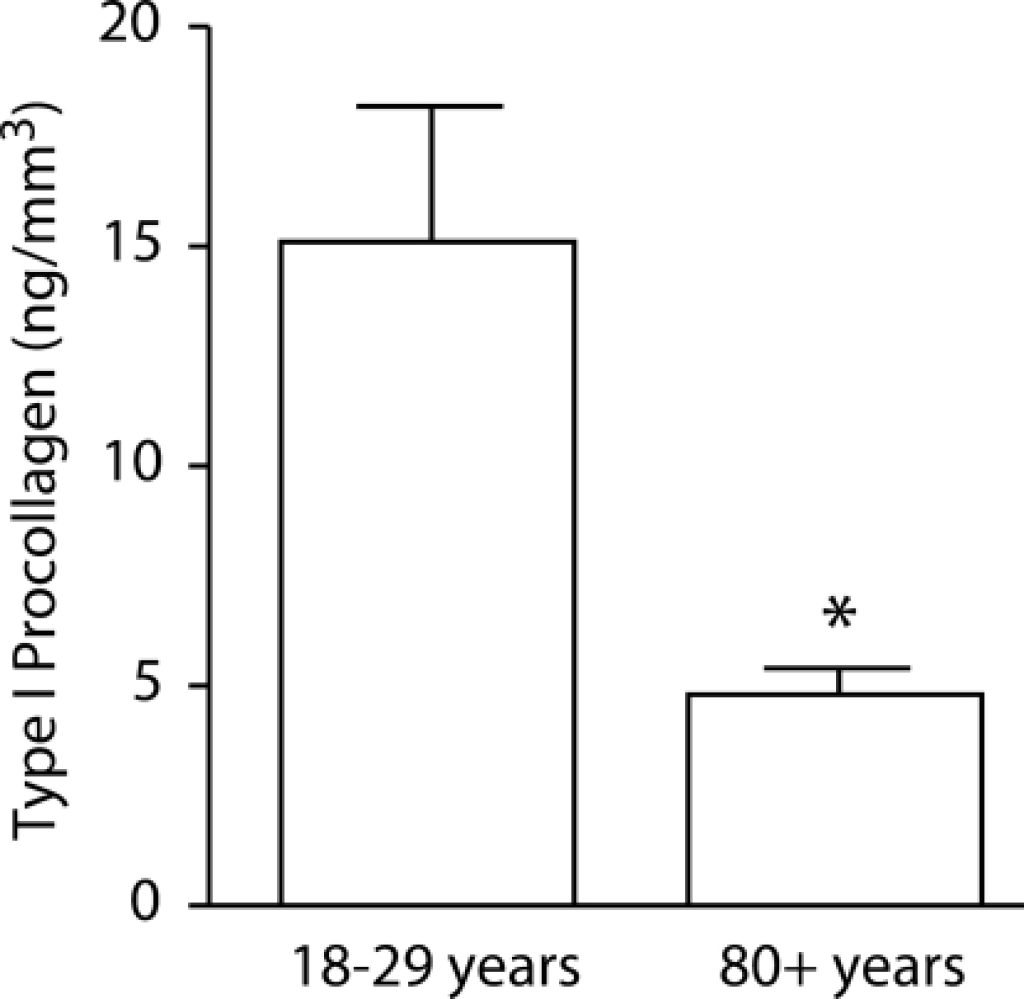
The biomarker for collagen synthesis decreases as you age. Procollagen type I production in young and old skin. The values shown are averages SEM of six young and six old people. The Student’s t-test was used to determine the statistical significance of the differences between young and old skin. *Statistically significant at the P 0.05 level.
How to restore collagen
Restore collagen levels through Diet
To prevent wrinkles and other signs of skin aging, a large number of people investigate collagen-boosting products. However there are a number of other ways to improve collagen levels in the body without spending a ton of money on collagen products.
Dietary sources of vitamin C
Vitamin C is essential vitamin for hyaluronic acid synthesis. Hyaluronic acid can reduce recovery time, alleviate joint pain and restore hydration to the skin. Without adequate vitamin C, the body will not receive the full benefits of hyaluronic acid synthesis.
According to one study, hyaluronic acid can stimulate collagen production in the human body. As both hyaluronic acid and collagen are essential for skin, consuming foods rich in vitamin C and amino acids can increase the levels of hyaluronic acid and collagen in the body. Vitamin C-rich foods include oranges, red peppers, kale, Brussels sprouts, broccoli, and strawberries.
Bone Broth
Bone broth is a good source of collagen as collagen is extracted from beef, chicken, or fish bones to create a flavorful liquid that can be consumed straight or used in other dishes. Most bone broth recipes call for simmering bones in water for one or two days on the stovetop or in a slow cooker.
The impressive collagen content of bone broth is arguably the primary reason why individuals consume it. Nearly one-third of our total protein is collagen, which is primarily found in our skin, tendons, cartilage, and bone. Collagen literally holds us together, and bone broth strengthens collagen.
In addition to being rich in collagen, bone broth also contains important amino acids such as glycine, proline, and glutamine. Glycine functions as a neurotransmitter in our brains, whereas proline is essential for protein synthesis, metabolism, wound healing, immune system function, and other processes. Glutamine maintains intestinal and immune health.
Restore collagen levels through Supplements
Collagen Supplements
Collagen supplements are used to improve joint and skin health. According to a 2021 study taking hydrolyzed collagen supplements for 90 days can reduce wrinkles while also improving skin elasticity and hydration (2).
Furthermore, the authors of a 2020 study discovered that collagen peptides in supplements have a direct effect on fibroblasts which mediate important signals for cell regeneration and repair processes (3,4). Fibroblast has a relevant role in anti-aging therapy because it is related to collagen and elastin synthesis activation responsible for skin resistance and elasticity, characteristics that are diminished with skin aging.
Restore collagen levels through Topical
Bakuchiol and retinol have been scientifically researched to increase collagen production in the skin8, thereby reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles*. They accomplish this by speeding up your skin’s natural turnover cycle. When this occurs, you have more healthy, fully functional skin cells; these young cells are more capable of producing collagen (5,6).
Glycolic acid when applied topically, this has been shown to increase collagen production (7). It is believed to accomplish this by inducing a reparative healing response in the skin, which stimulates collagen production.
Restore collagen levels through Lifestyle
Control stress.
Stress causes an increase in hormones such as cortisol, which, according to research, can reduce collagen production (8). In addition, when we are under stress, our bodies redirect nutrients to organs such as the lungs and brain, meaning that the skin receives fewer resources to produce a healthy quantity of collagen.
Sleep zZZzz… Get beauty sleep:
The REM cycle is when the body is able to perform the majority of its cellular rejuvenation, including collagen production. The skin experiences an increase in HGH (human growth hormone) during this phase of the nighttime sleep cycle. The release of HGH aids in the regeneration of body tissues and stimulates the production of more cells to replace those lost each day.
Protect skin from Sun damage :
Practice smart sun care. Natural light is an indispensable component of a healthy lifestyle but too much can damage the skin resulting in pre-mature aging. Sunlight is one of the key contributors to skin aging. Wrinkles, age spots, loss of elasticity, dryness, various tumors, uneven skin structure – all these things appear due to years of poor protection from UV-radiation.
The skin consists of three layers: the epidermis, the dermis, and the subcutis, or basement layer. The dermis contains collagen and elastin, which support the structure of the skin. Due to these elements skin looks smooth and youthful. UV radiation from the sun deteriorates collagen and elastin over time. Damaged fibers lose their elasticity and ability to contract after being stretched, and the skin is no longer in good condition.
Work Cited :
Varani, J. “Decreased Collagen Production in Chronologically Aged Skin”. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1606623/
Nutr, J. “Ingested hyaluronan moisturizes dry skin”. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4110621/
Gancevicience, R. “Skin anti-aging strategies”. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3583892/
Miranda, R. “Effects of hydrolyzed collagen supplementation on skin aging: a systematic review and meta-analysis”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33742704/
Rodriguez, M I. “Collagen: A review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29144022/
Yang, L. “Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Influences Epidermal Homeostasis of Living Skin Equivalents through Affecting Fibroblast Phenotypes and Functions”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29847822/



